ENT Health for Seniors: Special Considerations
As we age, changes in our ear, nose and throat systems are common and
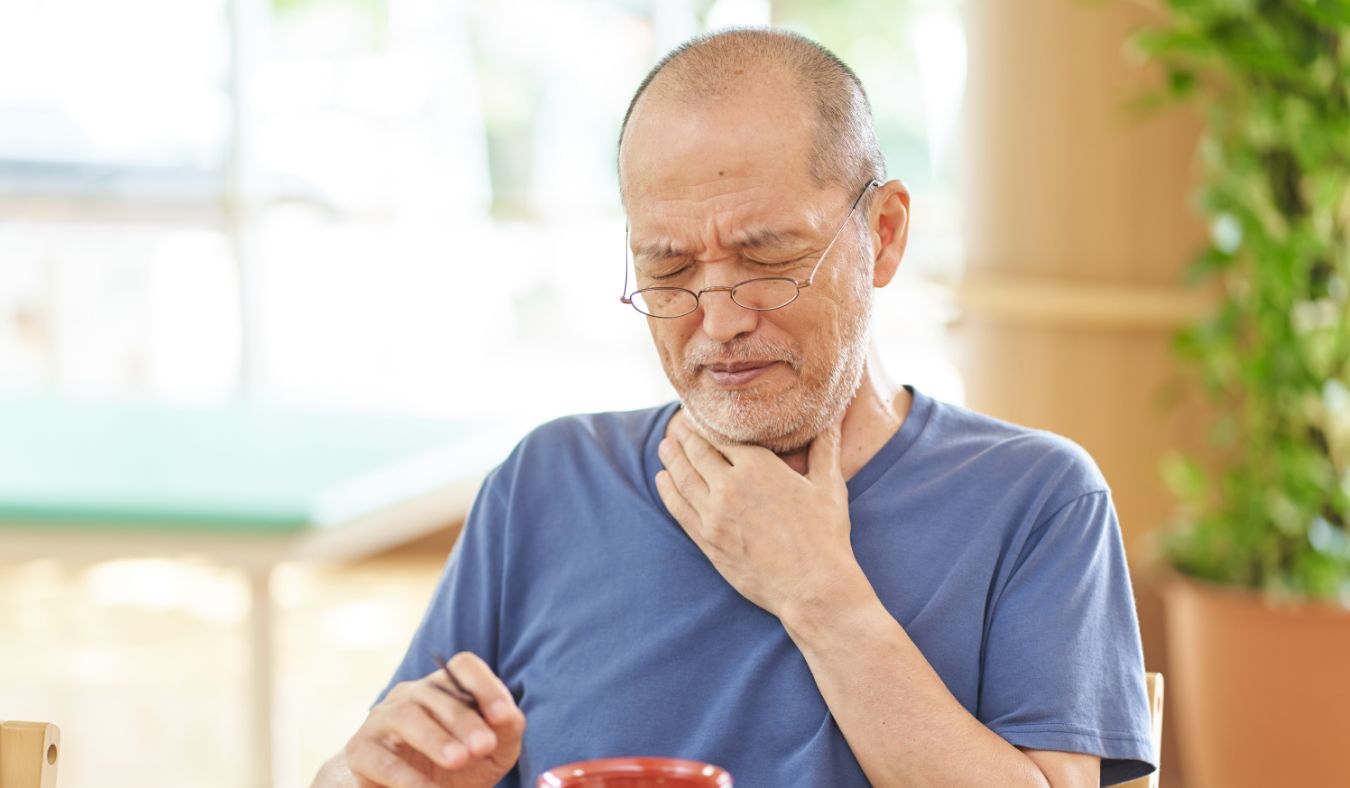


As we age, changes in our ear, nose and throat systems are common and
If you need ENT surgery, you’re probably concerned about how it will

Our voices do more than just carry our words – they express our